Rivanna3S Development Guide
This page is the main source for explanations about development decisions, and how implemented logic is meant to work at a high-level, for the Rivanna3S Embedded Codebase
For explanation on the underlying embedded real-time operating system, see the PhotonicOS page
Project Architecture
At a high level, the project is structured into folders as follows:
BottomDistBoard/,MotorBoard/,RelayBoard/,TelemetryBoard/,TopDistBoard/- these folders hold the application level code for each board. Consider each folder to be the application for that specific boardbuild/- compiled files, not tracked by Gitcmake/,CMakeLists.txt- configuration files for CMake (our build system)Common/- shared classes that can be used in any application codeCommon/Drivers/- classes that represent specific hardware (ex. Uart). These drivers are hardware-agnosticCommon/Libs/- classes that do not represent specific hardware (ex. a queue)Common/Libs/Inc/FreeRTOSConfig.h- configuration for the FreeRTOS kernel. Modifying this is dangerous, only modify with explicit Embedded lead permission!Common/can_structs/- contains the C CAN structs, which are generated from DBC filesCommon/startup.{cpp,h}- this is where the “real” main method is. After doing hardware init, it yields control toapp_main()in each application
Drivers/- for each supported microcontroller: STM HAL files and peripheral hardware init filesMiddlewares/- FreeRTOS and FatFs core code. We don’t modify any of this*.pyfiles - Python scripts with a common use in the development process. See here for info about compile, upload, and monitor
Note that some directories and files of lesser interest are not shown above.
Logging / Printing
Rather than using functions like printf(), we have log functions:
log_debug()for debugging messageslog_info()for informational messageslog_warn()for when something went wrong, but the car does not need to shutdownlog_fault()for when something went wrong, and the car needs to shutdown
These function all have standard printf() functionality, except for printing floats.
To read log messages, connect your laptop to the board, and run monitor.py. Note that the log must be configured before it can be used. In the example below, it is set to the info level, meaning any lower levels (in this case, only debug) will not be logged.
void app_main() {
log_configure(INFO_LVL, LOG_TX, LOG_RX, 921600);
// now we can log stuff
log_info("Starting...");
int val = 10;
log_debug("Value %d: " val); // will not be logged due to the log level set in `log_configure()`
log_fault("Battery fault detected!");
...
}
CAN
Controller Area Network is a commonly used serial protocol in the automotive industry. We use this as our main mode of data transmission between components of the car for 2 main reasons:
- Multiple devices can be connected at once. Many serial protocols only support having 2 connected devices at once, like UART.
- All nodes can send and receive messages without central coordination. This removes the need for a ‘central’ hub node, unlike protocols using a Master-Slave Topology like I2C.
There are 2 other benefits as well that come with CAN by default, but could be easily replicated and are common:
- A robust error handling system for when messages fail to send or are corrupted.
- The hardware specification is built on differential signaling, which greatly reduces the impact of electrical noise and voltage supply imperfections.
Terminology
- Node: any device on the CAN network
- CAN bus: the physical communication network
- CAN network: the high-level concept of the CAN bus with all its nodes attached
- CAN frame: a serialized CAN message
- CAN message: data and identifier, in a human-readable format
- Signal: a specific piece of data in a CAN message, like a throttle value
- CAN Transceiver: special hardware that converts logic signals to and from the CAN bus’s physical specification
Defining CAN messages
Each of our CAN messages is defined in a DBC file. This file specifies what data a given CAN message will hold and its identifier; CAN messages cannot be defined ad-hoc, they must meet an already defined specification.
Our Messages are defined here. We use the Python package cantools to read and write CAN messages in Python, and to generate the C structs for each message used in the Embedded Codebase.
Sending and receiving CAN messages in the Embedded Codebase
Start off by defining a CAN Interface at the top of main.cpp for that board.
CanInterface main_can = CanInterface(CAN_TX, CAN_RX, CAN_STANDBY, 250000, CanNetwork::Main);
To send a message, create a CAN struct of the specific message you are sending. Then call .write()
PedalStatus msg{};
msg.throttle_pedal = 10;
msg.brake_pedal = 0;
main_can.write(&msg);
To receive a message, create a function that accepts a const SerializedCanMessage reference as the sole argument, and returns nothing. Note that you will want to deserialize msg immediately if you are doing anything with the structure of the CAN message’s data.
void handle_dashboard_commands(const SerializedCanMessage &msg) {
DashboardCommands cmd{};
cmd.deserialize(&msg);
// do stuff with cmd...
}
You must also register this function with the CAN Interface, so it knows to call the function when receiving a certain message type. This should be done in the app_main() function
main_can.register_callback(DashboardCommands::get_message_ID(), handle_dashboard_commands);
See Common/Libs/Inc/CanInterface.h for full details. Note that this architecture is new for Rivanna3S; Rivanna3 and earlier use a very different architecture.
Rivanna3S CAN Networks
The current CAN networks are as follows:
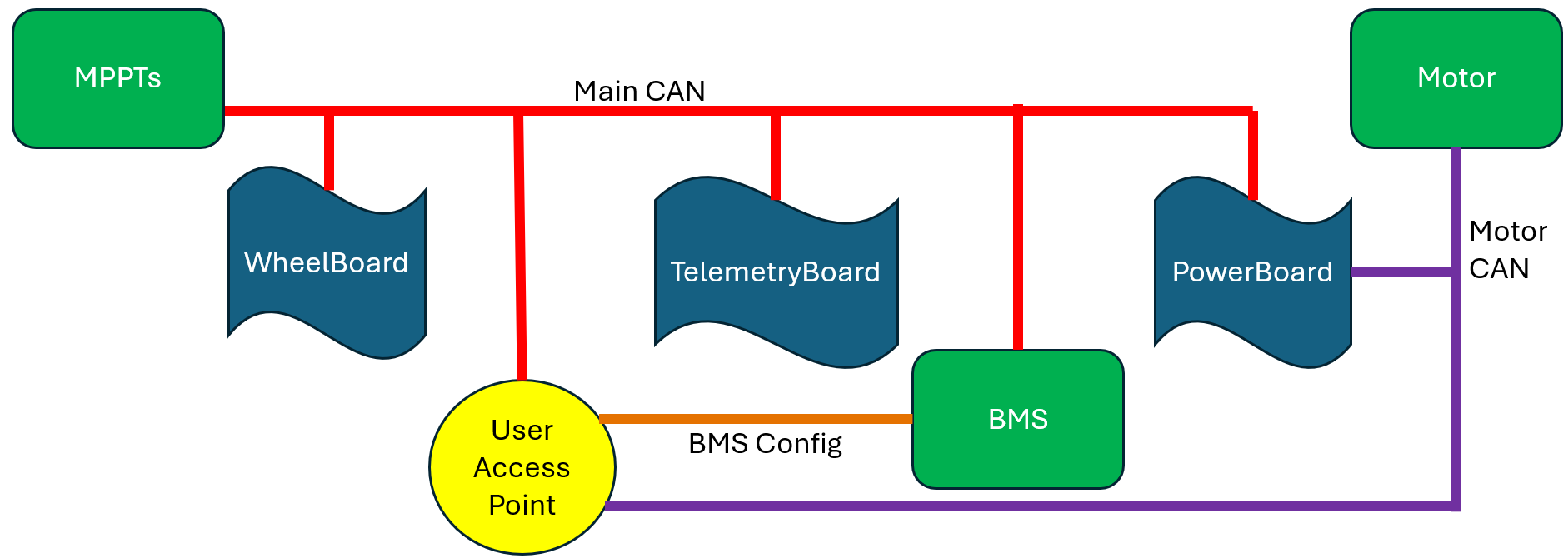
- Main CAN - almost everything is attached to this network, when people say ‘the CAN network’ they mean main CAN
- Motor CAN - connects the motor controller and the PowerBoard
Precharge
TODO: update for Rivanna3S, current info is from Rivanna3
Precharge is a system used on the high-voltage part of the car’s electrical system to prevent inrush current. This section refers to the motor, but also applies to the MPPTs as well. Precharge logic and hardware is managed by the Power Subteam; Embedded only implements the logic in software.
Theory
When the motor is connected to the HV system, the circuit can be modeled as a simple RC circuit, because of the inherent capacitance and resistance of the motor. The time taken to charge the capacitor is proportional to resistance * capacitance. By the inherent motor properties, the time constant is small, and the inherent resistance is very small. This results in very high current when the motor is first energized, as the capacitor is charging fast with little resistance; this is known as inrush current, which is bad because it causes extra wear and tear on the motor.
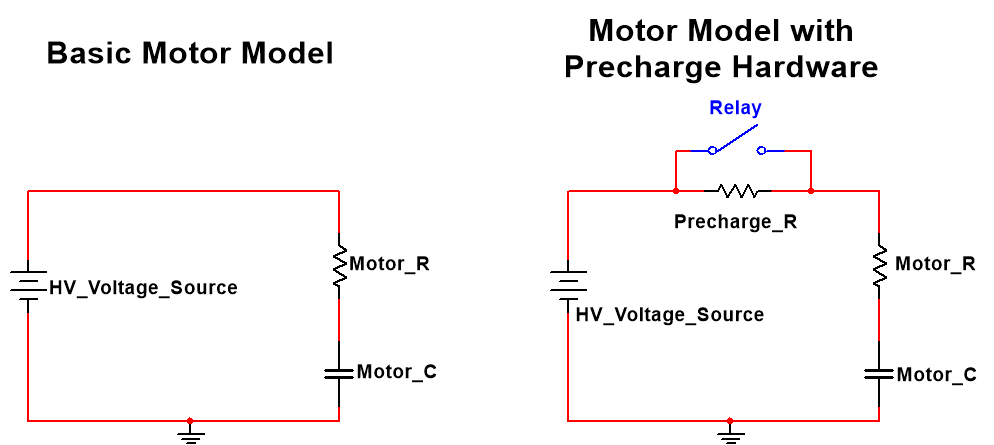
The solution: Add another resistor in series to increase the time constant, and therefore reduce the magnitude of current. This resistor is in parallel with a relay (switch) to enable and disable (short it) it, because:
- The resistor should be enabled when first energizing the motor, to reduce inrush current.
- The resistor should be disabled when the motor is in operation, so the motor can quickly draw the current it needs; the time constant must be minimized for the motor to be responsive.
Embedded implements the logic that controls this relay.
Normal Logic
- Wait until contactor 12 rising edge.
- Wait until discharge_relay_status is high (this signal is sent by the BMS over CAN in the BPSPackInformation message).
- Close (enable) motor precharge enable.
- Wait until discharge RC voltage is greater than 95% of pack_voltage (this signal is sent by the BMS over CAN in the BPSPackInformation message).
- Close (enable) discharge contactor, wait a small delay, open (disable) motor precharge enable.
Note that the process as described is for motor precharge, but MPPT precharge is the same process, just with discharge and motor variables replaced with charge and MPPT variables. Both motor and MPPT precharge processes happen concurrently and independently.
Fault Logic
If at any time (before, during, or after precharge) contactor 12 has a falling edge or a fault occurs elsewhere, then open (disable) the charge and discharge contactor and the motor and MPPT precharge enable relays.
Cruise Control
TODO: update for Rivanna3S, current info is from Rivanna3
Cruise control is a common car feature that makes the car drive at a constant speed. For Rivanna3S, cruise control is implemented using the PID Algorithm. PID works by setting the output of the motor based on 3 constants. The PID constants can be found in PowerBoard/lib/include/CruiseControl.h. These should be tuned if cruise control is not effectively reaching the target speed. See PID without a PHD for more information on tuning and PID theory.
Driver Usage
The cruise control target speed can be changed by the driver. There are buttons that increase, decrease, and toggle cruise control. Cruise up / down change the target speed by a constant set in PowerBoard/lib/include/CruiseControl.h, which is currently set to 5mph.